Debt Mutual Funds are Better than Fixed Deposits
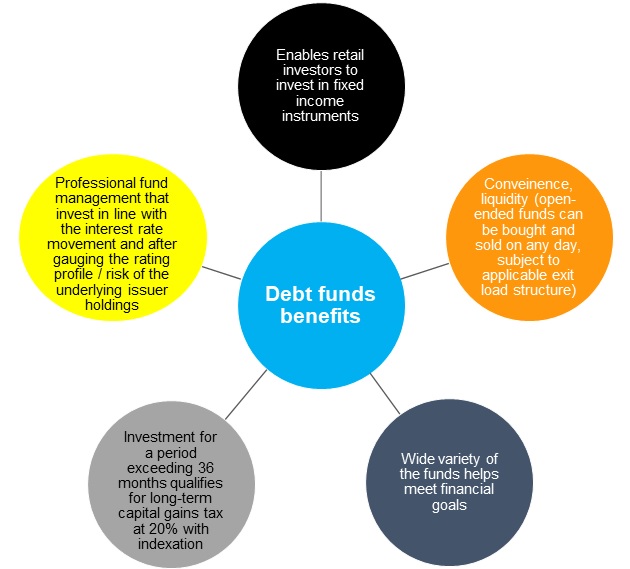
Debt mutual funds have emerged as an apt alternative to traditional investment options, such as bank fixed deposits, thanks to their ability to give mark-to-market (MTM) returns and indexation benefit for an investment horizon of over three years as per the current tax laws.

Fixed Deposits (FD) are not just investments, they are a part of Indian tradition and culture. What most people don’t realize is that they can earn more interest with similar levels of risk by investing in debt funds instead of FD.
But now debt funds are becoming an increasingly widespread rival to the hallowed FD.
A debt fund is a type of mutual fund which invests most of the money gathered from investors into fixed income instruments like corporate bonds, government bonds (both state and central), bonds issued by banks, certificate of deposit, treasury bills etc. These mutual funds are best for investors who are risk averse in nature and do not wish to invest in stock market.
Various Debt Fund Options
A debt fund invests in fixed-interest generating securities like corporate bonds, government securities, treasury bills, commercial paper and other money market instruments. The basic reason behind investing in debt fund is to earn interest income and capital appreciation. The issuer pre-decides the interest rate you will earn as well as maturity period. That’s why they are called ‘fixed-income’ securities because you know what you’re going to get out of them.
Invest in Debt Fund instead of Fixed Deposit
There was a time when every extra cash – bonus, increment – went on to become FDs. Our grandparents, parents have all ended up in investing in FDs at least once in their lifetime. It was the best option to earn interest while ensuring capital protection. What changed? Over the past few years, mutual funds have come to the core. As a result, FD is no longer considered as the most popular long-term investment goal.
The declining interest rate regime and the excessive liquidity caused by last year’s demonetization have forced banks to reduce their FD interest rates to historic lows. This, in turn, is forcing many retail investors to turn towards smarter investment alternatives like debt mutual funds.
Why invest in Debt Funds?
Debt funds are the closest which comes to the conventional FDs in terms of risk. A debt fund’s main goal is to give investors steady income after the maturity period. So, you must choose a time horizon in line with that of the fund.
You can find out about various debt funds and their duration directly from the fund houses or online or through a third-party. This will help investors understand a fund’s performance with respect to interest and return rates. It will also make it easier for you to avoid market volatility by making informed decisions.
Returns on Investment
After demonetization, many banks lower the FD rates due to excessive liquidity. State Bank of India (SBI), for example, currently offers 6.9 % for 1-year deposits, compared to 8% in 2015. For a 3 year deposit, it is even lower at 6.60%.
Debt funds have historically given returns in the range of 7-9% per annum.
As the returns of debt funds demonstrate, you can beat the banks by investing in debt funds. Debt fund investors assume both credit risk and interest rate risk and are hence compensated by higher returns.
Taxation on Debt Funds and Fixed Deposits
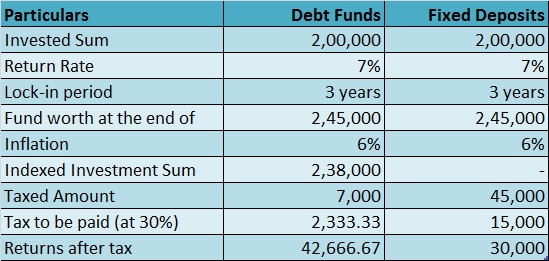
You must add the short-term debt fund gains (less than 3 years) to your income and they are taxable as per your tax slab rate. For long-term gains, there is a 20% after the indexation benefits. As for fixed deposit returns, you can add it to your income and it will be taxed accordingly.
The main difference between this two low-risk investment instruments is that of taxation.
In case of Fixed Deposits (FD)
The interest earned from FDs is added to your annual income for taxation purposes. Hence, the tax rate on interest earned from FDs will depend on your income tax slab, i.e. 5 %, 20 % or 30 % on the interest received.
For example, if your annual income, after including interest earned from your FDs, falls within the 30% tax bracket, the interest component will attract 30% income tax. Since many investors are in the top tax bracket, this takes away a large chunk of their returns.
In case of Debt Funds
Taxes upon debt mutual funds are of two types depending upon the period for which they are held. These two types are:
Short-term Capital Gain Tax: This is applicable to debt mutual funds held for a period of 36 months or less i.e. anything less than 3 years. In short-term capital gain tax, tax on funds is calculated as per income tax slab of the individual, i.e. 5%, 20% or 30% on the amount of gain.
Long-term Capital Gain tax: This is applicable to debt mutual funds held for a period of 36 months or more i.e. anything more than 3 years. In long-term capital gain tax, tax on funds is calculated at the rate of 20 % with cost indexation on the amount of gain.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
Apart from above mention taxation, banks also deduct TDS on interest income from fixed deposits. It was introduced to collect tax at the source from where an individual’s income is generated.
As per the Income Tax Act, any company or person making a payment is required to deduct tax at source if the payment exceeds certain threshold limits. TDS has to be deducted at the rates prescribed by the tax department.
As a resident Indian, there will be no TDS when you sell/redeem your debt fund units. You are required to show the income and pay taxes, if any when you file your returns.
Great Liquidity when cash flow is required
Turning to liquidity, open-ended debt funds proceeds are credited within a period of 2-3 working days depending on factors such as whether an Electronic Clearing Services (ECS) mandate is registered. FDs are also typically available at 1-2 day’s notice, but usually, carry a penalty if they are redeemed before the maturity date.
Banks penalize premature withdrawal of FDs by paying lower interest rate than the original booked interest rate. Premature withdrawal is however not allowed in tax saving fixed deposits as they have a lock-in period of 5 years.
Most banks currently deduct 1% from the original booked rate or 1% from the original card rate applicable for the period for which the FD has been in force, whichever is lower. These may adversely impact your FD’s effective rate of return in case of pre-mature withdrawal during emergencies.
Debt mutual funds, other than Fixed Maturity Plans, do not restrict redemption. However, many funds charge exit loads, ranging from 0.25–1% of the redeemed amount, if they are redeemed within a pre-specified period. Such periods can range anywhere from 15 days to 6 months.
Ultra short-term and many short-term funds do not charge exit loads. Such debt funds will suit best to park your emergency fund
Risk Associated
Bank FDs can be rightly considered as one of the safest avenues for parking your surpluses. The reason is that Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), an RBI subsidiary, guarantees all bank deposits of up to ₹ 1 lakh in the event of your bank’s failure.
The coverage extends to all types of bank deposits, including fixed, savings, current and recurring deposits.
Debt funds are relatively less risky than equity funds, but they are not risk-free like the way bank FDs are. Though they invest in government securities, money market instruments, and corporate deposits, the investors are still exposed to the risk of default or bankruptcy of concerned parties. This makes it riskier as compared to traditional Fixed Deposits.
But, the risk associated with debt funds is slow low, it is comparable to that of fixed deposits.
For short-term goals and low risk appetite
Investors with a low risk appetite aiming to build an emergency fund or having short-term goals, such as children’s tuition fees and settlement of one-time bills, can invest in liquid funds instead of a savings account as the former has the potential to generate better returns at reasonable liquidity.
Investors with a low risk-bearing capacity and short-term horizon (from a day to a week) can choose overnight funds. Investors with a slightly higher risk-bearing capacity can consider investing in ultra short-term funds and low duration funds. Note, short duration funds typically do well in a rising interest rate scenario and they are less sensitive to interest rate changes.
For medium- to long-term goals and ability to bear moderate to high risk
There are short to medium duration funds with an investment horizon of 1 to 4 years. Further for investors with a high-risk appetite intending to invest for a medium to long term, debt funds like gilt funds, dynamic and long duration funds etc. with investment horizon of 4 years and above are available.
Meanwhile, investors with the ability to take risk or the affinity to invest in corporate bonds can look at credit opportunity and corporate bond funds / banking and PSU funds. A credit risk fund invests minimum 65% of its assets in corporate bonds which shall not be highest rated instruments, while a corporate bond fund invests minimum 80% in highest rated corporate bonds.
In addition, investors can consider fixed monthly plans (FMPs), which resonate with bank deposits. FMPs follow a buy-and-hold strategy which can help investors lock-in higher yields for the entire investment period. FMPs are close-ended debt funds with varying maturity tenures starting from three months to five years. Investors can only invest in or enter at the time of a new fund offer (NFO) period. Investors wishing to exit may do so, through the stock exchange where the FMP is listed. Redemption of the units of the FMPs is not allowed prior to the maturity of FMP. FMPs can generate higher tax-adjusted returns because of the benefit of indexation (adjusting gains after considering inflation) for a holding period of more than three years.
Evaluate underlying risk factors before investment
While debt funds offer a good opportunity to investors with a low risk profile, they do come with some risks. That notwithstanding, investors should evaluate all schemes based on the underlying risk factors and map them onto their risk-return profile and investment horizon.
Ultimately, you should weigh your decision on your risk appetite, time horizon, and investment goals. Therefore, when the market looks positive and you notice several prospects for economic growth, it makes sense to opt for debt funds than fixed deposits.
Apart from the above, certain other risks to which the debt mutual funds are exposed to are reinvestment risk, regulatory risk, currency risks, risk associate with investment in derivatives, foreign instruments, etc, depending on the investment objective and the strategy of the fund. Investors shall always refer to the Scheme Information Document and Key Information Memorandum carefully to understand the detailed risk factors associated with the particular mutual fund schemes.
Debt funds clearly outscore bank FDs in terms of returns, liquidity, investment options, various types and tax treatment.
Bank FDs outscored debt mutual funds only in terms of capital protection and certainty of returns. However, if debt funds are selected wisely, even these risks can be mitigated to a large extent.
Ultimately, you should weigh your decision on your risk appetite, time horizon and investment goals. As market looks positive in last few years and there is several prospects for economic growth in coming years with the announcement of Union Budget 2018, it makes more sense to opt for debt funds than fixed deposits.
For your regular allocation to debt, which will remain for more than 3 years, debt funds make a better choice thanks to their consistent long-term track record, tax efficiency and flexibility to shift.
Don’t invest in debt funds without doing your homework. Performance track record along with scheme-specific attributes, portfolio credit quality, fund manager track record and expense ratios really do matter.
Mutual Fund investments are subject to market risks, read all scheme related documents carefully.